Understanding Your Water Intake: Myths and Reality
Written on
Chapter 1: The Dangers of Overhydration
Consuming excessive amounts of water can lead to severe health issues, including seizures, coma, and even death. While it may seem startling to ask how much water could be harmful, it's a reality worth considering.

During my past struggles with reflux, I initially blamed my water consumption. After researching, I realized my hydration habits were not ideal, and my daily intake of about eight glasses was based on a common misconception.
Myth 1: The 8 Glasses Rule Each individual's hydration needs vary significantly based on factors like age, weight, physical activity, diet, health conditions, and gender. Additionally, environmental conditions play a role; those in hot and humid climates require more fluids. Dr. Huang warns that adhering to the "eight glasses" guideline can be risky, especially for individuals with heart or kidney issues, as excessive water can lead to serious complications.
Section 1.1: Thirst Doesn't Always Mean Dehydration
Contrary to popular belief, feeling thirsty doesn't necessarily indicate dehydration. Dehydration occurs from natural water loss through sweat, tears, and respiration. Your kidneys regulate thirst, and a loss of 2-3% of body weight can signal the need for more fluids.

Myth 2: Coffee Leads to Dehydration While caffeine is often labeled as a diuretic, recent studies show that the water content in coffee typically balances out its dehydrating effects.
Myth 3: It's Impossible to Overhydrate Drinking more water than your body can manage can lead to hyponatremia, or water toxicity, which disrupts sodium levels. Symptoms may include confusion, nausea, migraines, and in extreme cases, death. Individuals with existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable to these risks.
Section 1.2: Signs of Overhydration
So how can you tell if you're consuming too much water?
- Urine Color: Ideally, your urine should be straw yellow. Clear urine may indicate overhydration, while deep yellow suggests dehydration.
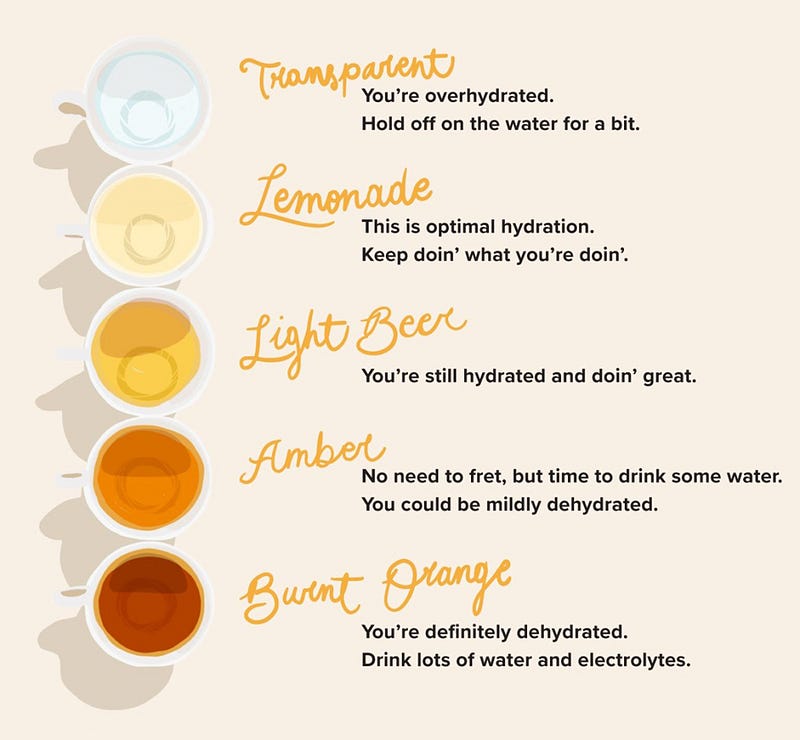
On average, you should urinate about seven times a day, though factors like climate and activity levels can influence this.
- Headaches and Nausea: Excessive fluid can lead to swelling in cells, causing headaches and nausea as the body struggles to eliminate the surplus water.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired may be a sign of your kidneys working overtime to filter out excess fluid.
- Muscle Cramps: An imbalance in electrolytes due to overhydration can result in muscle weakness and cramping.
Water toxicity is less of a concern for individuals without underlying health issues, as healthy kidneys can generally manage excess fluids effectively.
How to Determine Your Ideal Hydration Level To ensure you're adequately hydrated, consider the following indicators: - You rarely feel thirsty. - Your urine is light yellow or nearly clear.
Because everyone’s needs differ based on size, location, and activity, monitoring urine color over time can help you establish your optimal water intake.
Remember, hydration is not just a short-term concern; water is essential for your body, comprising 50% to 70% of your weight. Always consult a healthcare professional if you have questions or concerns about your hydration levels.
Chapter 2: Myths Debunked
In the first video, Dr. Berg discusses why the belief in needing to drink eight glasses of water daily is a myth, providing insights into proper hydration.
The second video addresses common mistakes people make when drinking water, helping viewers understand how to stay properly hydrated without overdoing it.
Thank you for reading! If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment and consider supporting me by joining Medium using my referral link.